The Medici family are called the Godfathers of the Renaissance because they laid the groundwork for cultural prosperity in Florence. Their major innovations in banking, art, and architecture persist today.
The Medici family is one of the most powerful and influential dynasties in European history. They introduced new banking systems and laid the groundwork to make Florence a cultural hotspot of Renaissance Italy. Through their political strategy and patronage of major artists, such as Michelangelo, they shaped the High Renaissance and the Italian political landscape. Read on to discover how the Medici family established their power and maintained their influence over hundreds of years.
The Medici Family’s Rise to Power
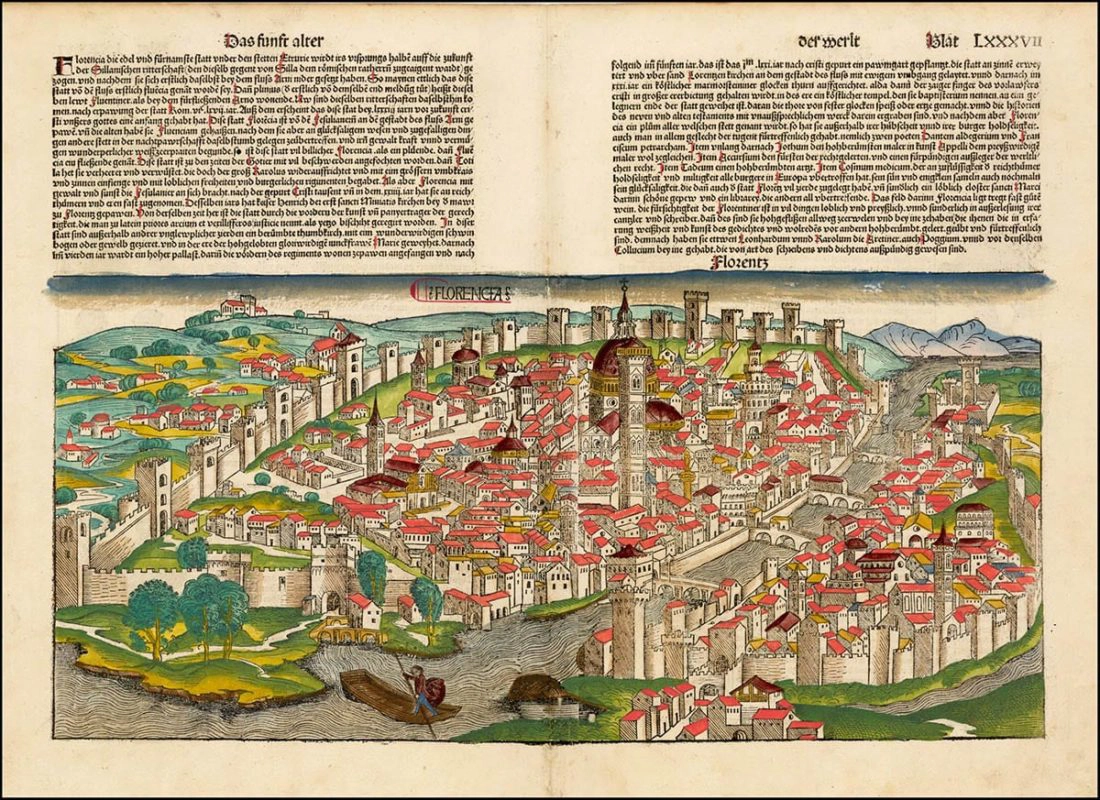
Italy was not a unified (and independent) nation when the Medici family’s power began. The Italian peninsula was organized into city-states, unlike surrounding nation-states, such as France. Some of these states included Siena, Venice, Naples, and Florence; the last of which is where the Medicis established their political power base.
The peak of their power lasted from 1434 to 1737, producing figures who would extend their hold beyond Florence. These include four popes: Leo X, Clement VII, Pius IV, and Leo XI. Among the Medici family members were also two queens of France: Catherine de’ Medici and Marie de’ Medici.
The basis of the Medicis’ wealth and prestige was their bank. Active from 1397 to 1494, it was the largest credit institution in 15th-century Europe.
After Giovanni di Bicci de’ Medici founded the bank in Florence in 1397, his son, Cosimo the Elder (1389-1464), expanded the family business.. He opened branches in other key city-states, including Geneva, Venice, and Rome, where the Papal States would task him with the management of the papal treasury.
In his lifetime, Cosimo would eventually go on to establish branches in foreign cities, including London, Bruges, and Lübeck. These offices made it easy for the papacy to order goods across Europe and for bishoprics to pay fees from afar.
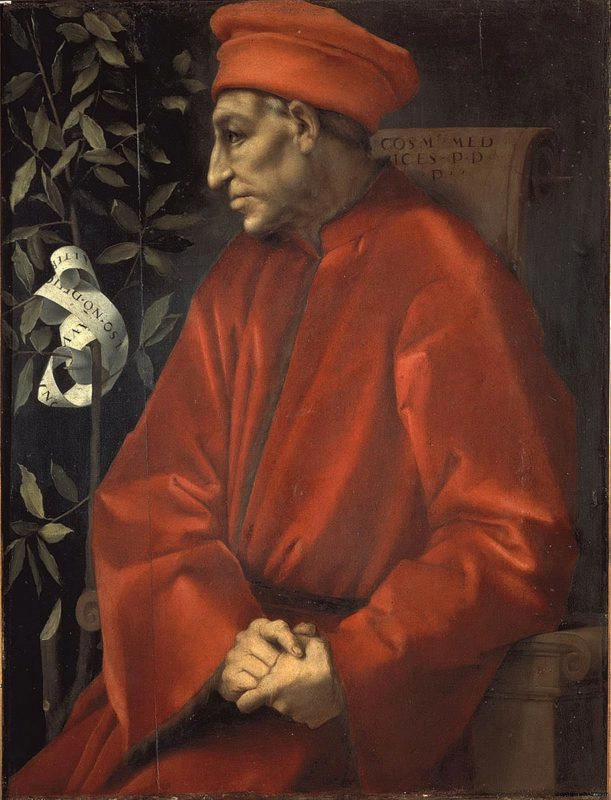

Location is just one part of what made the Medici Bank prestigious. The Medicis also developed some of the financial tools we still use today. They introduced Double-Entry Bookkeeping, a practice that involves recording a payer’s debits and credits in a single log. This made it easier and more accurate to calculate one’s net worth.
Additionally, the Medici Bank introduced the Letters of Credit. At the time, it was dangerous to send large sums of money across the continent to pay for foreign goods. The Letters of Credit fixed this problem. In practice, this could look like an Englishman paying a London branch of the bank in pounds for an art piece from Florence. The Florentine office would then produce a Letter of Credit to the artist as proof of future payment. Then, the artist could deliver the work and take his payout from the bank in his own currency.
These achievements eventually helped the Medicis become one of the wealthiest families in Europe.















